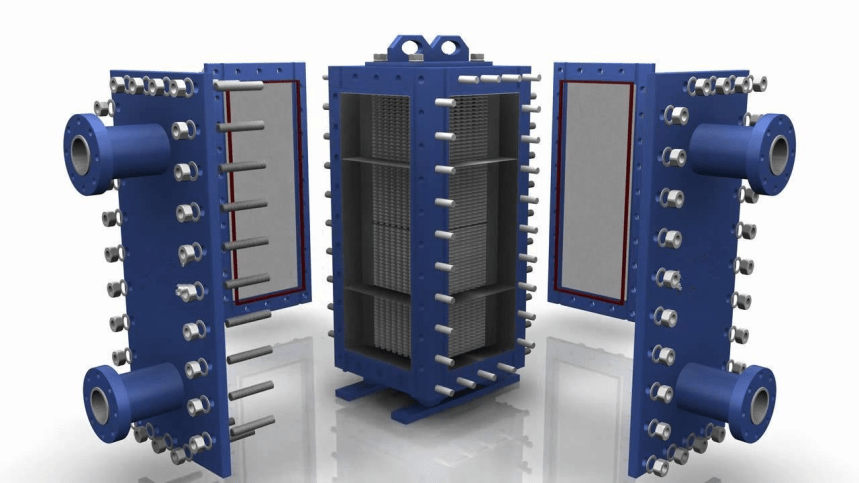
What is a plate heat exchanger?
Plate heat exchanger is a high-tech device designed to efficiently transfer heat energy between different liquids or vapours. Its design is based on thin metal plates assembled into a package. Each plate has a special corrugated surface, which increases the contact area of the heat transfer fluids and ensures intensive heat transfer.
Why are plate heat exchangers so popular?
They are distinguished by their compact size, high efficiency, configuration flexibility and ease of maintenance. Compared to traditional tube heat exchangers, plate models achieve a significantly larger heat transfer area in a smaller volume.
The applications for plate heat exchangers cover a wide range of industries, from food processing to chemicals. They are used for heating, cooling, pasteurisation, evaporation and other technological processes.
How it works
The heat exchange process in a plate heat exchanger is carried out by contact between two heat transfer fluids separated by a thin metal plate. The heat transfer fluids move alternately through the channels between the plates, transferring heat to each other through the plate wall.
Advantages of plate heat exchangers
High heat transfer efficiency: Due to the large contact area of the heat transfer fluids and the thin plate wall, heat transfer is fast and efficient.
Compact size: They take up significantly less space than tube heat exchangers.
Flexibility: The heat exchanger configuration can be tailored to specific process parameters (number of plates, corrugation type, material).
Easy cleaning and maintenance: The collapsible design makes it easy to disassemble the heat exchanger for cleaning from deposits.
Wide range of operating temperatures and pressures: The use of different materials for the plates allows for operation with aggressive media and high temperatures.
Materials
A variety of materials are used to make the plates of plate heat exchangers, such as stainless steel, titanium, and alloys. The choice of material depends on the type of heat transfer medium, temperature, pressure and other process parameters.
Applications in various industries
Food industry: Cooling of milk, juices, beer, pasteurisation of food, evaporation.
Sugar industry: Heating and cooling of syrups, evaporation.
Pulp industry: Heating and cooling of water and other working fluids, chemical recovery.
Feed industry: Pasteurisation of feed, cooling of products.
Chemical industry: Heating and cooling of aggressive media, vapour condensation, heat recovery.
Conclusion
Plate heat exchangers are versatile and efficient heat transfer equipment for a wide range of industries. Their high efficiency, compactness, flexibility and ease of maintenance make them indispensable in modern technological processes.
Prospects for the development of plate heat exchangers are associated with the use of new materials, the development of innovative designs and the expansion of applications.